Less Known Signs and Symptoms of ADHD
Day 7 of Unlocking the Mysteries of ADHD In this…
Day 7 of Unlocking the Mysteries of ADHD
In this episode, I will touch on Symptoms of ADHD in a little more detail. More specifically, some of the symptoms that can go overlooked. So, without further ado, let’s soar high and explore the depths of understanding ADHD together.
What Are Symptoms of ADHD
One common symptom is difficulty paying attention or staying focused on tasks or activities. People who have ADHD often find it challenging to:
- Follow Through on Instructions
- Stay Organized
- Complete Tasks
Some of us may also:
- Frequently Lose Things
- Be Easily Distracted by External Stimuli
- Struggle With Maintaining Attention During Conversations or Activities
Another Symptom of ADHD Is Impulsivity
People with ADHD often act without considering the consequences. It is important to remember that these actions are not intentional and that we are often unaware of them. We should be kind to ourselves and acknowledge that our symptoms sometimes cause us to behave in certain ways unintentionally.
It is common for people with ADHD to act without thinking about what they are about to say and whether it could be misinterpreted.
With That Said, We May Struggle With Things Like:
- Interrupting Others During Conversations
- Have Difficulty Waiting Turn
- Engaging in Impulsive Behavior
- Talking Excessively
- Taking Risks Without Considering Potential Dangers
Additionally, someone with ADHD may display hyperactivity symptoms, although not everyone has the hyperactive symptoms.
Symptoms can sometimes cause problems such as:
- Fidgeting or Squirming When Seated for Prolonged Periods of Time.
- Restlessness or an Inability to Stay Still When Expected to Do So.
- Excessive Talking and Difficulty Engaging in Quiet Activities.
Understanding these symptoms can help people recognize if they might have ADHD.
If you suspect that you may have ADHD, please seek a diagnosis and treatment from a healthcare professional who specializes in neurodevelopmental disorders such as ADHD.
What Are Some Lesser Known Symptoms of ADHD
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adhd-attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-included-definition-symptoms-traits-causes-treatment-5084784_final-bc92546bc9df465ea7f13fc423c2085b.jpg)
I. Hyperfocus and Obsessiveness
Understanding hyperfocus and its connection to ADHD
Hyperfocus is a phenomenon commonly associated with ADHD, but it often goes unnoticed or overlooked. It is characterized by an intense and prolonged concentration on a particular task or activity, to the point of losing track of time and surroundings. People with ADHD may experience periods of hyperfocus, where they become deeply engrossed in an activity that captures their interest. This can be both beneficial and problematic, as hyperfocus can lead to increased productivity and creativity, but it can also cause them to neglect other responsibilities or tasks.
To learn more about hyperfocus in relation to ADHD, you can visit this link.
Recognizing obsessive tendencies as a potential symptom of ADHD
Obsessiveness can also be a less known symptom of ADHD. Individuals with ADHD may exhibit obsessive tendencies, such as fixating on details or repeatedly engaging in certain behaviors. This obsession can manifest in various ways, such as constantly organizing or arranging objects, obsessively researching a particular topic, or having repetitive thoughts or rituals. It is important to note that occasional obsessiveness does not necessarily indicate ADHD, but when it becomes a pattern and significantly impacts daily functioning, it may be worth exploring as a potential symptom of ADHD.
For more information on the connection between ADHD and obsessive behaviors, you can refer to this resource.

II. Sensory Overload
Exploring the link between ADHD and sensory processing issues
Recognizing the signs of sensory overload in individuals with ADHD
Sensory overload is a lesser-known aspect of ADHD that often goes unnoticed or overlooked. Many individuals with ADHD experience difficulty processing sensory information, leading to feelings of overwhelm and overstimulation. It’s important to recognize the signs of sensory overload in individuals with ADHD to provide appropriate support and accommodations. Some common signs of sensory overload include:
- Hypersensitivity to light, sound, touch, or smell
- Feeling overwhelmed in crowded or noisy environments
- Difficulty filtering out background noise or distractions
- Overreacting to sensory stimuli
- Avoidance of certain textures, tastes, or smells
Individuals with ADHD may also exhibit specific behaviors when experiencing sensory overload, such as:
- Covering their ears or eyes to block out sensory input
- Seeking sensory input through fidgeting or repetitive movements
- Becoming irritable or agitated in response to sensory stimuli
- Withdrawal or social isolation in overwhelming situations
Recognizing these signs and understanding the link between ADHD and sensory processing issues can help individuals with ADHD and their loved ones better manage their symptoms and provide necessary support.
To learn more about sensory processing issues and ADHD, you can visit this article on ADHD and Sensory Overload from ADDitude Magazine.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adhd-in-girls-symptoms-of-adhd-in-girls-20547_v2-67d95b323e7340e9ba5bf8aa7152cdd7.gif)
III. Emotional Dysregulation
Uncovering the emotional symptoms of ADHD
ADHD is commonly associated with difficulties in attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. However, there is another aspect of ADHD that often goes unnoticed – emotional dysregulation. Here are some less known or overlooked signs and symptoms of emotional dysregulation in individuals with ADHD:
- Intense and frequent mood swings: People with ADHD may experience sudden and unpredictable shifts in their emotions, going from happy to angry or sad within a short period.
- Rejection sensitive dysphoria: This is a term used to describe an extreme sensitivity to criticism or perceived rejection. Individuals with ADHD may have intense emotional responses when they feel criticized or rejected, even if the situation does not warrant such a reaction.
- Difficulty regulating emotions: Individuals with ADHD may struggle to manage and control their emotions effectively. They may have difficulty calming down when upset or controlling their anger when frustrated.
- Impulsive emotional reactions: Emotional dysregulation can lead to impulsive emotional responses. People with ADHD may react without thinking in the heat of the moment, which can often result in regrettable actions or words.
- Trouble coping with stress: Stressful situations can overwhelm individuals with ADHD, causing emotional distress and difficulty coping with the demands of everyday life.
Understanding the highs and lows of emotional dysregulation in ADHD
It is important to note that emotional dysregulation in ADHD can manifest differently in each individual. Some may experience intense anger, while others may struggle with sadness or anxiety. Understanding these emotional highs and lows is crucial for individuals with ADHD and those around them.
Managing emotional dysregulation in ADHD often involves a combination of strategies, such as:
- Psychoeducation: Learning about ADHD and emotional dysregulation can help individuals and their loved ones better understand and manage the symptoms.
- Therapy: Engaging in therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or dialectical behavior therapy, can provide individuals with ADHD valuable tools and coping mechanisms to regulate their emotions effectively.
- Medication: In some cases, medication prescribed by a healthcare professional may help reduce emotional dysregulation symptoms.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals with ADHD calm their minds and regulate their emotions.
By recognizing and addressing the often overlooked signs and symptoms of emotional dysregulation in ADHD, individuals can find effective ways to manage their emotions and improve their overall well-being.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-SydneySaporito-RejectionSensitiveDysphoria-Standard-e6a2c95b5b124de0be17471550b726dc.jpg)
IV. Rejection Sensitivity
Defining rejection sensitivity and its impact on individuals with ADHD
Rejection sensitivity is a less known but significant aspect of ADHD that can have a profound impact on individuals’ lives. It refers to an intense emotional response to the perception or anticipation of rejection. People with ADHD often experience heightened sensitivity to rejection, which can lead to feelings of anxiety, self-doubt, and social withdrawal. This can significantly impact their relationships, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Recognizing the signs of rejection sensitivity in relationships and everyday life
It’s essential to recognize the signs of rejection sensitivity to better understand and support individuals with ADHD. Some common signs may include:
- Overanalyzing social interactions and seeking reassurance from others
- Fear of criticism or disapproval, even in minor situations
- Avoidance of social situations to prevent potential rejection
- Difficulty handling constructive criticism or negative feedback
- Quick emotional reactions to perceived rejection, such as anger, sadness, or withdrawal
By recognizing and understanding rejection sensitivity, individuals with ADHD and their loved ones can work together to develop effective coping strategies and create a supportive environment. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can also be beneficial in managing and navigating the challenges associated with rejection sensitivity in ADHD.
Remember, every individual’s experience with ADHD is unique, and it’s essential to approach these discussions with empathy and understanding. Supporting individuals with ADHD in managing rejection sensitivity can make a significant difference in their overall well-being and quality of life.

V. Time Blindness
When it comes to ADHD, there are several lesser-known signs and symptoms that often go overlooked. One such symptom is time blindness, which refers to the difficulty individuals with ADHD have in perceiving the passage of time accurately. Here are some important points to understand about time blindness and its impact on individuals with ADHD:
- Concept of Time Blindness: Time blindness is a common symptom of ADHD where individuals struggle with accurately estimating the duration of time. They may find it challenging to gauge how long tasks take or the ability to follow a schedule.
- Challenges of Time Management: Time blindness can lead to significant challenges in time management for individuals with ADHD. They may often underestimate how long tasks will take, leading to poor planning and difficulty meeting deadlines.
- Impacts on Daily Life: Time blindness can affect various aspects of daily life for individuals with ADHD. It can lead to difficulties in completing assignments on time, being punctual for appointments, and organizing daily routines effectively.
- Problems with Prioritization: Due to time blindness, individuals with ADHD may struggle with prioritizing tasks and allocating appropriate time to each activity. This can result in procrastination, feeling overwhelmed, and decreased productivity.
- Strategies for Managing Time Blindness: Fortunately, there are strategies that can help individuals with ADHD better manage time blindness, including:
- Setting alarms or timers to help keep track of time.
- Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable chunks with set time limits.
- Utilizing visual aids such as calendars, planners, and schedules.
- Seeking support from a therapist or coach specializing in ADHD management.
It’s important to recognize that time blindness is a real and significant challenge for individuals with ADHD. By understanding this symptom and implementing effective strategies, individuals can improve their time management skills and overall quality of life.
For more information on ADHD and its symptoms, you can refer to the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Wikipedia page.
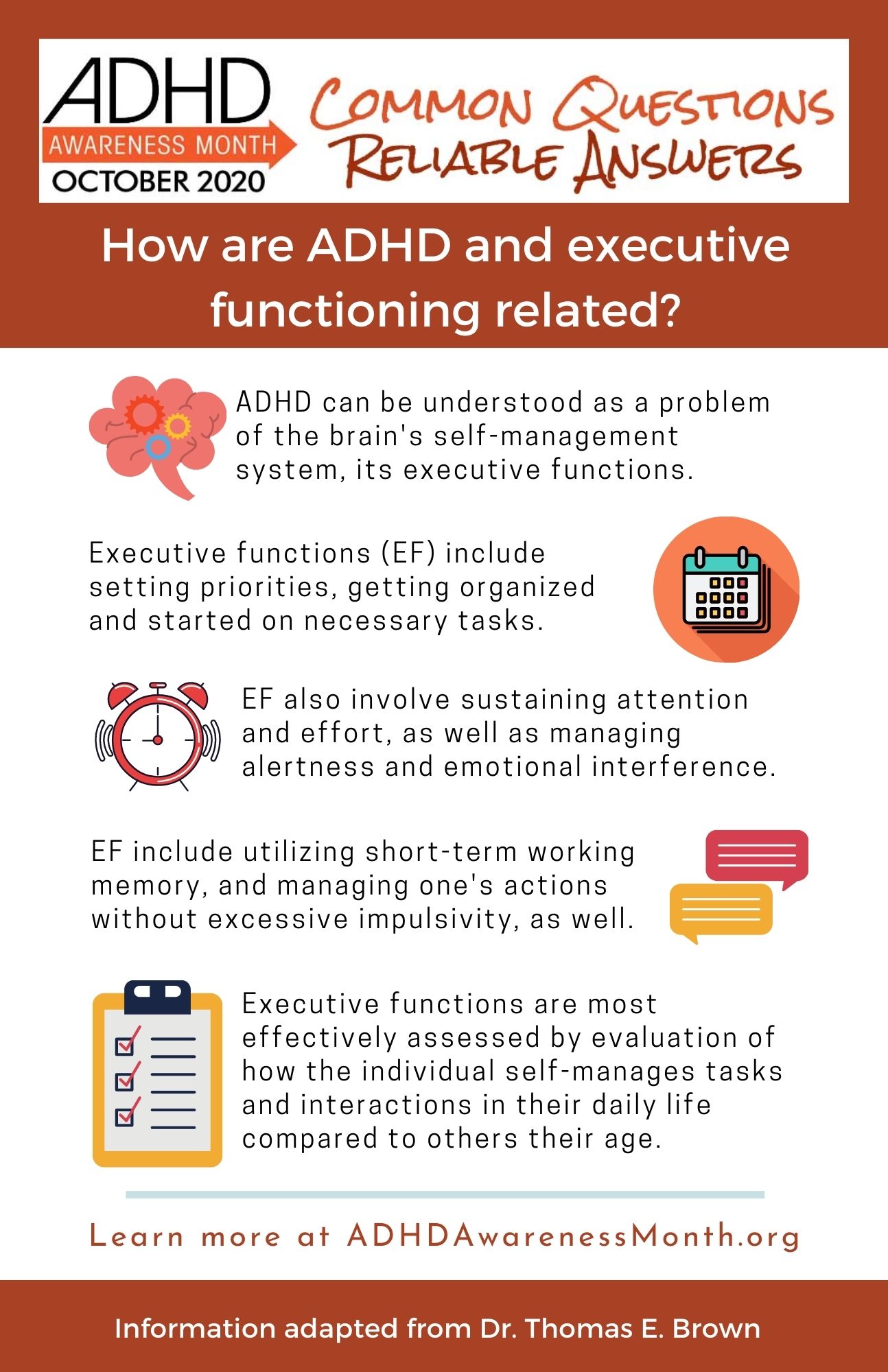
VI. Executive Dysfunction
Defining executive dysfunction and its role in ADHD
Executive dysfunction is a term used to describe difficulties with the brain’s executive functions, which include tasks such as organizing, planning, initiating tasks, staying focused, and managing time. It is a common symptom of ADHD that is often overlooked or misunderstood. Executive dysfunction can significantly impact a person’s daily life and their ability to perform tasks efficiently.
People with ADHD may struggle with:
- Organizing and prioritizing tasks
- Planning and following through with long-term goals
- Initiating tasks and staying motivated
- Managing time and being punctual
- Maintaining focus and avoiding distractions
Recognizing the impact of executive dysfunction on daily life and tasks is crucial in understanding the challenges faced by individuals with ADHD. It is essential to provide them with the support and accommodations they need to navigate their daily responsibilities more effectively.
Sources:

VII. Impulsivity beyond Actions
Understanding the different forms of impulsivity in individuals with ADHD
When it comes to ADHD, impulsivity is often associated with impulsive actions like interrupting others or making impromptu decisions. However, there are other forms of impulsivity that are less known but equally important to recognize and understand. These include impulsive thoughts, words, and decisions. It’s essential to be aware of these aspects to better support individuals with ADHD and create a conducive environment for them to thrive.
Recognizing impulsive thoughts, words, and decisions
It’s not uncommon for individuals with ADHD to experience impulsive thoughts, where ideas or judgments come to mind without much consideration or reflection. Some may find it challenging to filter and control these fleeting thoughts, leading to a constant stream of impulsive ideas.
Similarly, impulsive words can be a challenge for individuals with ADHD. They may blurt out comments or statements without thinking, which can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or unintended consequences. It’s crucial to cultivate patience and understanding when interacting with someone who has ADHD, as they may not always have full control over their impulsive speech.
Lastly, impulsive decisions can also be a characteristic of ADHD. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with impulsivity when it comes to making choices or judgments, particularly in situations that require careful consideration. This can sometimes result in hasty decisions that they may later regret.
Recognizing and understanding these less known forms of impulsivity is crucial in providing support and empathy to individuals with ADHD. By acknowledging and being mindful of these challenges, we can foster a more inclusive and understanding environment that allows individuals with ADHD to thrive and reach their full potential.

VIII. Difficulties with Task Initiation and Completion
Exploring the challenges of starting and finishing tasks for individuals with ADHD
When it comes to ADHD, there are some lesser-known or overlooked signs and symptoms that can impact an individual’s daily life. One of these is difficulties with task initiation and completion. This section will delve into the challenges faced by individuals with ADHD in starting and finishing tasks and provide insights into recognizing the signs.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Procrastination: Many individuals with ADHD struggle with getting started on tasks, often finding themselves putting them off until the last minute.
- Lack of Focus: Difficulty maintaining focus on one task at a time can make it challenging for individuals with ADHD to complete tasks efficiently.
- Easily Distracted: External distractions or internal thoughts can divert their attention, making it harder to stay on track and finish tasks.
- Poor Time Management: People with ADHD may struggle to estimate how long tasks will take, leading to issues with prioritization and time allocation.
- Overwhelm or Hyperfocus: While some individuals with ADHD may find it difficult to start tasks, others may become hyperfocused on a specific activity, causing them to neglect other responsibilities.
Recognizing these signs can help individuals with ADHD seek appropriate support and strategies to manage these challenges effectively. It’s important to remember that everyone’s experience with ADHD is unique, and symptoms can vary.
For more information on ADHD and its symptoms, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.
Understanding and addressing the difficulties with task initiation and completion can significantly improve the daily functioning and overall well-being of individuals with ADHD. By recognizing these challenges and implementing strategies tailored to their specific needs, individuals with ADHD can enhance their productivity and achieve their goals.

IX. Chronic Procrastination
Understanding the link between ADHD and chronic procrastination
Chronic procrastination is often overlooked as a potential sign of ADHD. Many people with ADHD struggle with procrastination due to difficulties with executive functioning skills. Here are a few things to consider:
- Difficulty with time management: Individuals with ADHD often struggle with estimating how long tasks will take and organizing their time effectively.
- Getting easily distracted: People with ADHD may find themselves easily distracted by unrelated thoughts or external stimuli, making it difficult to stay focused on tasks.
- Lack of motivation: A lack of motivation can be a common symptom of ADHD, leading individuals to delay tasks or avoid them altogether.
- Impulsivity: Impulsive behavior can lead to engaging in immediate gratification activities instead of prioritizing and completing important tasks.
It’s important to note that chronic procrastination can be a symptom of other conditions or simply a habit. If you suspect you or someone you know may have ADHD, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adhd-in-women-common-signs-and-symptoms-5211604-DD-V2-0d711bd73c7f4bfa808a200450bf5e30.jpg)
Poor Working Memory
Defining working memory and its impact on individuals with ADHD
Working memory is a cognitive function that allows us to temporarily hold and manipulate information in our mind while performing tasks. It plays a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives, such as learning, problem-solving, and organizing thoughts.
Individuals with ADHD often struggle with poor working memory, which can significantly impact their ability to concentrate, follow instructions, and complete tasks efficiently. It can hinder academic performance, job productivity, and even interpersonal relationships.
Recognizing the signs of poor working memory in daily life and academic/work settings
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have poor working memory due to ADHD, here are some signs to look out for:
- Difficulty remembering and following multi-step instructions
- Forgetting important deadlines and appointments
- Struggling to stay focused during conversations or lectures
- Frequently misplacing or losing items, such as keys or wallets
- Poor organization skills and difficulty prioritizing tasks
- Difficulty holding information in mind while performing mental calculations or problem-solving
In academic or work settings, individuals with poor working memory may exhibit the following behaviors:
- Difficulty staying on track with assignments and projects
- Trouble understanding and retaining new information quickly
- Inconsistent performance, with peaks and valleys in productivity
- Procrastination and needing frequent reminders or prompts
- Overlooking important details or making careless errors
It’s important to remember that the presence of these signs does not necessarily mean someone has ADHD or poor working memory. However, if these difficulties persist and significantly impact daily life or academic/work performance, it is advisable to seek professional evaluation for a comprehensive assessment.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of poor working memory can lead to early intervention strategies and support, enabling individuals with ADHD to better manage their challenges and reach their full potential.
Reference:

XI. Conclusion
Promoting awareness of lesser-known signs and symptoms of ADHD
In conclusion, it is essential to promote awareness of lesser-known signs and symptoms of ADHD. While many people are familiar with the classic symptoms like hyperactivity and impulsivity, there are other subtler indicators that may go unnoticed but still affect an individual’s daily life. By recognizing and understanding these lesser-known signs, individuals, parents, and educators can seek the appropriate support and interventions for those with ADHD. It is crucial to remember that ADHD manifests differently in each person, so being knowledgeable about all the possible signs can lead to better understanding and support for those affected.
